双曲函数
一般三角函数是基于圆的,在直角坐标系统点(x,y)满足圆方程。
x²+y²=1。
如果把加号改为减号,即
x²-y²=1。
移项,得
x²=y²+1,
所以
y=±√(x²-1),
即分段函数
y=√(x²-1),(x≤-1) ①
y=-√(x²-1),(x<-1) ②
y=√(x²-1),(x≥1) ③
y=-√(x²-1)。(x>1) ④
①②连成一条曲线,③④也连成一条曲线,两条曲线对称,与双曲线比较相似,用它实现的三角函数就是双曲函数了(注意了,没有“线”字)。

acosh(x)
返回 x 的反双曲余弦值。定义域[1,inf],值域[0,inf](双曲函数第一象限)。

计算公式:
![]()
>>>from math import acosh,inf,sqrt,log
>>>acosh(1.0), acosh(2.0), acosh(inf)
(0.0, 1.3169578969248166, inf)
>>>acosh(-1.0)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ValueError: math domain error
>>>acosh(10),log(10+sqrt(10**2-1))
(2.993222846126381, 2.993222846126381)
asinh(x)
返回 x 的反双曲正弦值。定义域[-inf,inf],值域[-inf,inf]。计算公式:
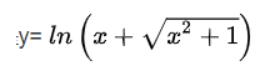
>>>from math import asinh,inf,sqrt,log
>>>asinh(0.0),asinh(2.0),asinh(inf)
(0.0, 1.4436354751788103, inf)
>>>asinh(-0.0),asinh(-2.0),asinh(-inf)
(-0.0, -1.4436354751788103, -inf)
>>>asinh(10),log(10+sqrt(10**2+1))
(2.99822295029797, 2.99822295029797)
atanh(x)
返回 x 的反双曲正切值。定义域(-1,1),值域(-inf,inf)。计算公式:
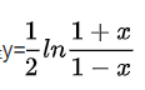
>>>from math import atanh,inf,sqrt,log
>>>atanh(-.999),atanh(0),atanh(.999)
(-3.8002011672501994, 0.0, 3.8002011672501994)
>>>atanh(.99999999999),log((1+.99999999999)/(1-.99999999999))/2
(13.01079156037454, 13.01079156037454)
cosh(x)
返回 x 的双曲余弦值。定义域[-inf,inf],值域[1,inf]。计算公式:
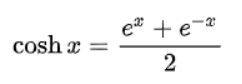
>>>from math import cosh,inf,exp
>>>cosh(-inf),cosh(0),cosh(inf)
(inf, 1.0, inf)
>>>cosh(10),(exp(10)+exp(-10))/2
(11013.232920103323, 11013.232920103324)
sinh(x)
返回 x 的双曲正弦值。定义域[-inf,inf],值域[-inf,inf]。计算公式:

>>>from math import sinh,inf,exp
>>>sinh(-inf),sinh(0),sinh(inf)
(-inf, 0.0, inf)
>>>sinh(10),(exp(10)-exp(-10))/2
(11013.232874703393, 11013.232874703393)
tanh(x)
返回 x 的双曲正切值。定义域[-inf,inf],值域[-1,1]。计算公式:

>>>from math import tanh,inf,exp
>>>tanh(-inf),tanh(0),tanh(inf)
(-1.0, 0.0, 1.0)
>>>tanh(10),(exp(10)-exp(-10))/(exp(10)+exp(-10))
(0.9999999958776927, 0.9999999958776926)
特殊函数
erf(x)
返回 x 处的误差函数(error function,如下图)的值 。

定义域[-inf,inf],值域[-1,1]。计算公式(积分函数):

>>>from math import erf,inf
>>>erf(-inf),erf(-1),erf(0),erf(1),erf(inf)
(-1.0, -0.8427007929497149, 0.0, 0.8427007929497149, 1.0)
误差函数erf()可以用来计算像累积标准正态分布这样的传统统计函数:
·
·
·
·
·
from math import erf,sqrtdef phi(x): '''Cumulative distribution function for the standard normal distribution''' return (1.0 + erf(x / sqrt(2.0))) / 2.0
在《五行星Python几何画板》中作图如下视频:
,时长00:30
erfc(x)
返回 x 处的互补误差函数。互补错误函数定义为 1.0 - erf(x)。如果采用定义的方法,当 x 值较大时,减法会导致有效位数的损失。该函数采用不同的算法,避免这种情况的发生。
>>>from math import erf,erfc
>>>erfc(0),1.0-erf(0)
(1.0, 1.0)
>>>erfc(1),1.0-erf(1)
(0.1572992070502851, 0.1572992070502851)
>>>erfc(2),1.0-erf(2)
(0.004677734981047266, 0.004677734981047288)
>>>erfc(4),1.0-erf(4)
(1.541725790028002e-08, 1.5417257914762672e-08)
>>>erfc(8),1.0-erf(8)
(1.1224297172982928e-29, 0.0)
gamma(x)
返回 x 处的伽马函数值。定义域(0,inf]。在实数域上伽玛函数定义为:

>>>from math import gamma,inf
>>>gamma(1e-10),gamma(1),gamma(inf)
(9999999999.422785, 1.0, inf)
lgamma(x)
返回Gamma函数在 x 处绝对值的自然对数。
>>>from math import gamma,lgamma,inf
>>>lgamma(1e-10),log(abs(gamma(1e-10)))
(23.025850929882736, 23.025850929882736)
>>>lgamma(1e-5),log(abs(gamma(1e-5)))
(11.512919692895824, 11.512919692895826)
>>>lgamma(1),log(abs(gamma(1)))
(0.0, 0.0)
>>>lgamma(100),log(abs(gamma(100)))
(359.1342053695754, 359.1342053695754)
>>>lgamma(200),log(abs(gamma(200)))
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
OverflowError: math range error
常量
math.pi
数学常数 π = 3.141592...,精确到可用精度。
math.e
数学常数 e = 2.718281...,精确到可用精度。
math.tau
数学常数 τ = 6.283185...,精确到可用精度。Tau 是一个圆周常数,等于 2π,圆的周长与半径之比。
math.inf
浮点正无穷大。(对于负无穷大,使用 -math.inf 。)相当于 float('inf') 的输出。
math.nan
一个浮点的 "非数字"(NaN)值。相当于 float('nan') 的输出。由于 IEEE-754标准的要求, math.nan 和 float('nan') 不被认为等于任何其他数值,包括其本身。要检查一个数字是否为NaN,请使用 isnan() 函数来测试 NaN ,而不是 is 或 == 。例子:
>>>import math
>>>math.pi
3.141592653589793
>>>math.e
2.718281828459045
>>>math.tau
6.283185307179586
>>>math.inf
inf
>>>math.nan
nan
>>>math.nan == math.nan
False
>>>float('nan') == float('nan')
False
>>>math.isnan(math.nan)
True
>>>math.isnan(float('nan'))
True
math模块主要是标准C语言数学库函数的简单包装。无效操作一般抛出ValueError异常,如 sqrt(-1.0) 或 log(0.0), 和结果溢出抛出OverflowError异常,例如, exp(1000.0) 。除非一个或多个输入参数是NaN,否则不会从本模块函数返回NaN;不过有例外,例如pow(float('nan'), 0.0) 和 hypot(float('nan'), float('inf')) 。
>>>import math
>>>math.sqrt(-1.0)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ValueError: math domain error
>>>math.log(0.0)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ValueError: math domain error
>>>math.exp(1000)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
OverflowError: math range error
>>>math.pow(float('nan'), 0.0)
1.0
>>>math.hypot(float('nan'), float('inf'))
inf